The human immune system is the term for all the ways that the body protects itself from dangerous outside microbes called pathogens. The most common pathogens that target human cells are bacteria and viruses. Without a functioning immune system, we become susceptible to diseases that we could otherwise easily defeat. We see examples of compromised immune systems in some people with HIV, a viral infection that cripples the immune system of its target and slowly kills through repeated infections. In other examples, such as autoimmune disease, the immune system mistakes its own tissue as foreign and attacks it. Over time, autoimmune diseases can be devastating for health.
Many factors play into how well an immune system works. Hormones, or the “endocrine system” as it is known in the medical community, have an important role in the immune system that we will explore in this article. We will also discuss the differences between men and women in terms of immunity, and how you can fortify your own immune system to keep yourself healthy.
How is the Immune System Regulated?
Like an anti-virus program for a PC, a human immune system requires constant “updates” to make necessary adjustments – for example, creating antibodies to combat specific emerging threats. The ongoing process of immune system regulation is called immunoregulation. In addition to the nervous system, the endocrine system is crucial for regulating immunity. The endocrine system’s role in the immune system primarily involves signaling to the various parts of the immune system throughout the body so that coordinated action can be taken.
The Role of Hormones in Immunity
Signaling hormone production, proliferation (division), and the release of immune system cells like lymphocytes and macrophages are the chief ways that hormones influence the immune system. The following hormones each have distinct roles in maintaining the immune system:
- The sex hormones (Testosterone, Estrogen, Progesterone)
- Prolactin
- Human Growth Hormone (HGH)
- Insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1)
- Thyroid hormones
- Vitamin D
Let’s shift focus to testosterone and its activity related to the immune system.
Testosterone’s Influence on the Immune System
Testosterone is referred to as “immunosuppressant” because it suppresses, or “tamps down”, the immune response. This relationship with the immune system exists in opposition to the “immunoenhancing” effect of estrogen, the female sex hormone, that stimulates the immune system.
Differences in Susceptibility to Disease Between Genders
The variant hormone levels between men and women have ramifications for disease development. Women are more susceptible to autoimmune disease than men because of their more responsive and sensitive immune systems. Conversely, men are more likely to experience illness caused by pathogens because of their relatively less active immune systems.
The essential differences between men and women in terms of immunity are due primarily to their divergent hormone levels, especially sex hormones like testosterone.
How does testosterone affect immunity? What could lower or higher levels mean for the strength and function of the immune system?
How Excessive Testosterone Affects Immunity
As the saying goes, too much of anything is bad. This piece of folk wisdom extends to circulating testosterone levels. Here is how excessive testosterone levels impact the immune system.
- Lower cytokine response
Cytokines are signaling molecules that mediate the immune response. They are extremely important for the overall immune function. Examples of cytokines are interferons, interleukins, lymphokines, chemokines, and tumor necrosis factors. In one study on men in Bolivia, higher testosterone concentrations in the blood correlated to lower cytokine levels.
- Lowered Immunity
Men get sick more often than women with pathogenic illnesses like the common cold. because of their higher testosterone levels. Previously, the reason for this disparity between the sexes was poorly understood. One fascinating piece of research sheds light on testosterone’s powerful effect within the immune system. Men in the study exhibited a lower immune response to a vaccine compared to their female counterparts, making them less resistant when they encountered the targeted virus in daily life.
Too much testosterone, as seen in bodybuilders who use steroids consistently, can wreak havoc on the immune system.
Testosterone levels steadily drop as we age. Here is a chart of the testosterone levels in men throughout life:
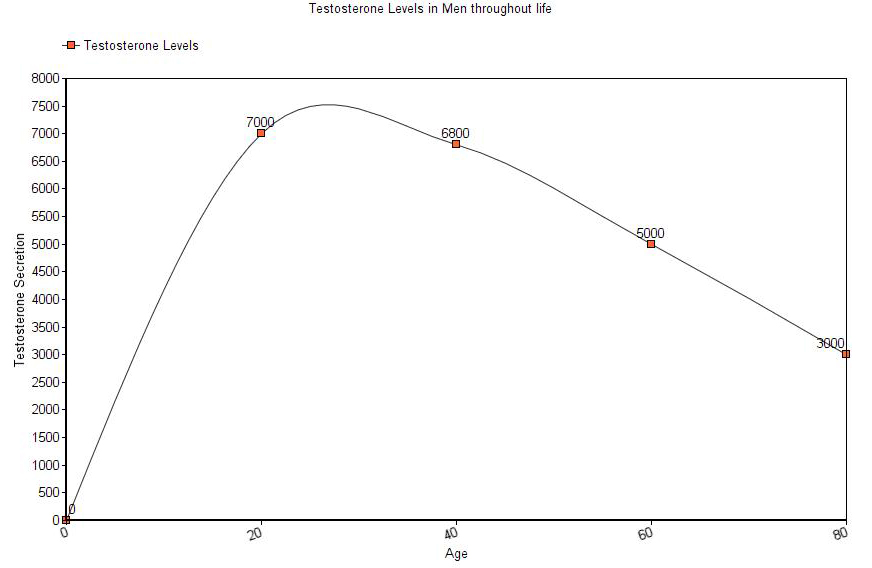
Low testosterone levels are just as undesirable for achieving a healthy immune system as levels that are too high.
How Inadequate Testosterone Affects Immunity
We’ve seen what testosterone exceeding normal levels can do to the immune system, but what about too little of the male sex hormone? Here is how less-than-ideal levels affect the immune system.

- Sleep Disturbances
One of the major complaints of patients who have low testosterone levels is an inability to fall asleep and stay asleep. Adequate sleep levels are critical for immune system function, as nearly all the necessary repair and maintenance work is done during sleep.

- Stress
Nothing short-circuits the immune system like uncontrolled stress. The study found that controlled stress responses, as a normal function of the “fight or flight” response to perceived threats, actually boosted immune function. However, higher levels of chronic stress, stress that is uncontrolled and persistent, correlated to impaired immune function. People who have abnormally low testosterone levels are much more likely to suffer from anxiety and depression as a result, hiking stress levels and, in turn, hampering the immune system.
Options for Managing Testosterone Levels
Fortunately for your immune system, managing testosterone levels is easier than ever before, thanks to a better understanding of the science of hormones and accompanying advances in medicine.
Slightly different strategies are suggested for men and women when it comes to achieving optimal testosterone levels.
Managing Testosterone for Men
Here are the best ways for men to manage their testosterone.
- Diet
More and more, the data hardens around the inescapable conclusion that diet is perhaps the single most important factor in maintaining health, including testosterone levels. Align your diet with your health goals by including plenty of fresh produce in your diet. In particular, cruciferous vegetables like broccoli and kale have potent testosterone-boosting effects because of a molecule called indole-3 carbinol. Vitamin D, abundant in fish and dairy, is also effective for raising testosterone levels. Getting plenty of zinc, found in shellfish and some nuts and seeds (particularly pumpkin seeds), is important also. Stay away from processed foods that kill testosterone.
- Physical Activity
Although any workout routine does great things for the hormonal system, weightlifting is by far the most effective exercise for supercharging testosterone levels.
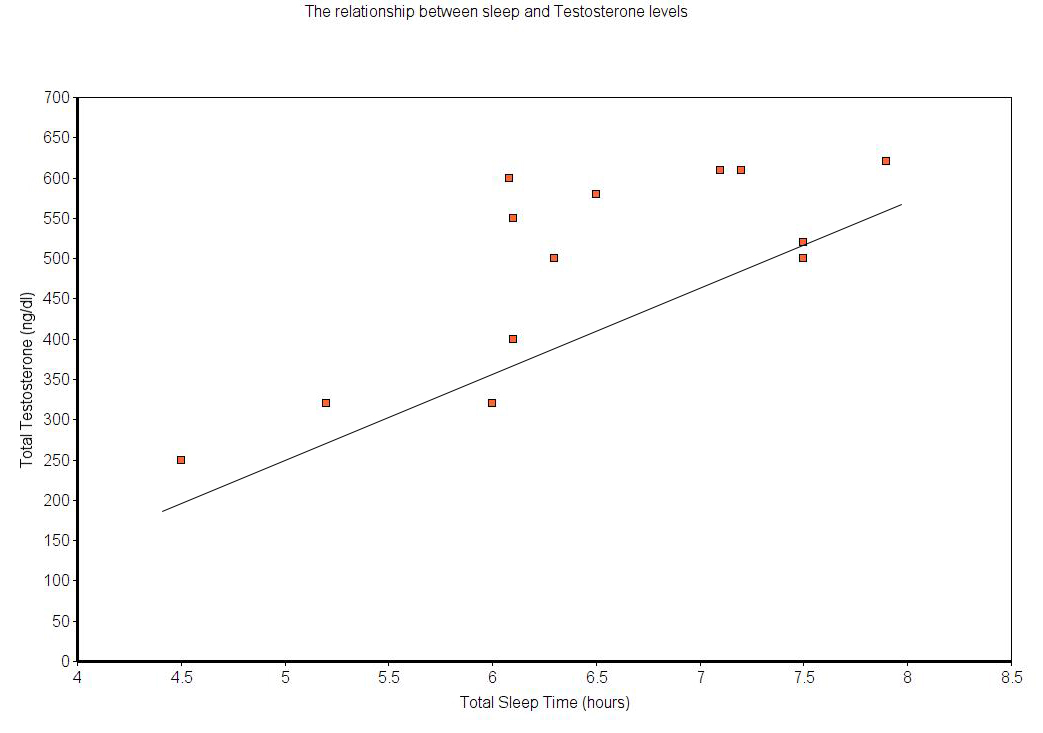
- Sleep
As we mentioned earlier, getting enough sleep is paramount, not just for a healthy endocrine system, but overall health. Here is a handy chart illustrating the relationship between sleep and testosterone levels.
- Testosterone Replacement Therapy (TRT)
TRT is a flagship procedure in one of the most exciting branches of medicine, hormone replacement therapy. A licensed provider measures the patient’s testosterone levels, titrates the correct dosage to achieve optimal levels, provides a quick injection, then measures level again after an appropriate time period to check progress.
These lifestyle adjustments, in addition to potential therapeutic administration of testosterone, can help men restore the hormone to ideal levels.
Managing Testosterone for Women
Women also produce and utilize testosterone, but in much smaller amounts than men. In women, testosterone is produced in the ovaries. Women going through menopause experience fluctuations in all their hormone levels, including testosterone. Here is how women can manage their testosterone levels.
- Diet. (see above)
- Physical Activity. (see above)
- Sleep. (see above)
- TRT for Women. Although TRT is not as popular for women as with men, it can still help women who have lower levels of testosterone. One of the main goals of TRT for women is to treat sexual dysfunction by increasing desire and satisfaction for women going through menopause.
Conclusions
Because of the close interconnection between the immune and endocrine systems, optimizing hormone levels, including testosterone, is a proven strategy for strengthening the immune system. A healthy set of immune cells that communicate with each other to coordinate disease-fighting activities is crucial for the body’s ability to thrive. Both women and men have an array of tools at their disposal to achieve hormonal balance, including TRT for low testosterone. Find out more about Testosterone replacement for men and women! Fill out the contact form and our experienced advisor will consult you for free.