Although the terms “growth hormone” and “steroids” might seem to be interchangeable terms to individuals not yet familiar with the differences, they are actually two completely unique hormones with vastly different activities in the body.
A large part of the confusion may be due to the fact that athletes commonly use (and abuse) both types of supplements. In turn, both HGH and steroids are banned in athletic competition. Many organizations such as the World Anti-Doping Agency regularly test athletes for illicit use.
 Nonetheless, there are vast differences between HGH and steroids worthy of exploration. Human growth hormone (HGH) is a naturally-occurring hormone manufactured in the brain in a structure called the pituitary gland. Optimal HGH levels are critical for several biological activities that we will discuss here.
Nonetheless, there are vast differences between HGH and steroids worthy of exploration. Human growth hormone (HGH) is a naturally-occurring hormone manufactured in the brain in a structure called the pituitary gland. Optimal HGH levels are critical for several biological activities that we will discuss here.
Steroids, on the other hand, are synthetically-produced molecular compounds that exert a variety of biological functions in the body. There are several types of steroids that we will discuss here.
So, what are steroids, what is growth hormone, and what are the key differences between them?
What Are Steroids?
As mentioned previously, the term “steroids” applies broadly to any compound with a characteristic set four rings in a particular arrangement. Contrary to popular belief, steroids actually occur naturally in an array of biological organisms, including plants, animals, and fungi.
In animals, steroids perform two types of work:
- Modulating membrane (cell wall) activity.
- Acting as signaling molecules, aka hormones.
It’s important to understand the difference between the various types of steroids. The two most prevalent types of steroids used in the US are:
- These are legitimate and recognized medicines frequently used in clinical settings to control swelling and inflammation. They work by exerting their potent immunomodulatory properties to calm the chronic inflammation seen in autoimmune conditions such as inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), multiple sclerosis, and many others.
- Anabolic steroids. Steroids are the types of steroids most commonly associated with the everyday use of the term, made famous by early pioneers in the sport of bodybuilding such as Arnold Schwarzenegger, Ronnie Coleman, and others.
In addition to offering different uses, the most important distinction between corticosteroids and steroids is that the former is legal with a prescription while the latter is fully illegal with no authorized medical uses. The Drug Enforcement Administration (DEA) notes that the internet, unsurprisingly, is the largest forum for buying and selling illegal steroids anywhere in the world.
Steroids, when injected through the veins, carry a number of serious side effects in addition to their muscle growth-promoting properties:
- Increased risk of heart attack or stroke.
- Shrinking of the testicles (hypogonadism).
- Decreased sperm production.
- Aggressive behavior.
- Acne (often severe).
- Male-pattern baldness.
- Unhealthy cholesterol levels.
- Tumor growth.
What Is HGH?
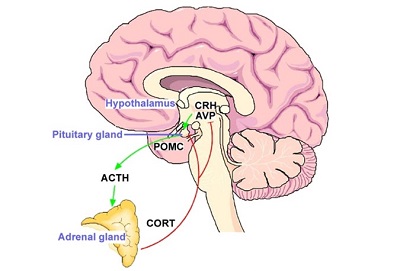 Human growth hormone (HGH or GH) is produced by the pituitary gland and released in pulsatile secretions, mostly at night during sleep. Although growth hormone may be most commonly associated with its growth-spurring function in children, HGH is actually critical for good health across the lifespan, even into adulthood.
Human growth hormone (HGH or GH) is produced by the pituitary gland and released in pulsatile secretions, mostly at night during sleep. Although growth hormone may be most commonly associated with its growth-spurring function in children, HGH is actually critical for good health across the lifespan, even into adulthood.
The pituitary gland makes up a portion of the so-called hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis (HPA axis), a vital component of the neuroendocrine system responsible for reacting to and managing stress in the body.
HGH itself, often working in combination with the liver-produced hormone insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1) is responsible for several key growth-related activities that include:
- Promoting greater lean muscle mass.
- Managing metabolic responses (i.e., blood sugar control)
- Regulating mental health (combatting depression and anxiety).
- Fortifying bone density.
Many factors may lead to a decline in HGH levels that may indicate the need for a clinical intervention to correct the imbalance through hormone replacement therapy (HRT).
Growth hormone levels might drop because:
- The pituitary gland is under-performing due to poor diet and/or lifestyle. Relevant factors such as diets saturated in processed foods, poor sleep quality, and lack of physical activity are shown to decrease HGH levels, often substantially enough to cause a diagnosable deficiency.
- Cancerous growths in or around the pituitary gland affect its ability to produce and/or secrete HGH.
- Inadequate blood supply is circulating to the pituitary gland, impairing its capacity to deliver HGH into the bloodstream.
Depending on the reasons for the HGH deficiency, supplementation with synthetic recombinant human growth hormone (rHGH), also known as somatropin, is often indicated to correct the imbalance in affected individuals.
What Are the Differences Between Steroids and HGH?
First of all, it’s worth re-emphasizing that somatropin (HGH) medications are legal to possess and use when authorized by a licensed physician who has issued a prescription to a patient. Anabolic steroids are purely illegal in all contexts.
 Secondly, although they are both hormones involved in the growth process, their effects on the body are vastly different.
Secondly, although they are both hormones involved in the growth process, their effects on the body are vastly different.
When a doctor performs the necessary screening processes to determine if a candidate with an HGH deficiency is suitable for therapy, the risks of serious side effects are minimal. Hormone replacement therapy with HGH is approved by the FDA and several reputable pharmaceutical manufacturers produce high-quality HGH (somatropin) supplements, including:
- Novo Nordisk (Norditropin).
- Merck (Saizen).
- Eli Lily (Humatrope).
- Sandoz (Omnitrope).
- Pfizer (Genotropin).
- Teva (Tev-Tropin).
These HGH medications are audited for purity and safety. Steroids, on the other hand, are not.
Why Are HGH and Steroids Often Confused?
There several reasons that HGH and steroids are often confused. The possible reasons that a person might mistake one for the other include the facts that:
- Both are anabolic, meaning that they spur muscle development (help to build muscle) – albeit in different ways with different side effects.
- Both steroids and HGH are usually administered via injection, a delivery method commonly associated in the popular imagination with synthetic performance-enhancing drugs.
- Many black-market producers of steroids also produce illegal (and often impure) HGH products to be sold under standard market value.
- Athletes commonly abuse both to reap the benefits of their performance-enhancing effects.
- Both sometimes are mistakenly promoted as a fountain of youth, but it’s fair to note that injectable HGH therapy really can give some signs of anti-aging effects.
The Dangers of Unprescribed HGH and Steroids
 Because steroids are only available for purchase on the black market, many are subject to tampering or adulteration. A study from the WHO found that one out of every ten medical supplies sourced from the Third World (a major supplier of illegal steroids in the US) is either fake or does not meet the quality standards of pharmaceutical-grade products like FDA-approved HGH.
Because steroids are only available for purchase on the black market, many are subject to tampering or adulteration. A study from the WHO found that one out of every ten medical supplies sourced from the Third World (a major supplier of illegal steroids in the US) is either fake or does not meet the quality standards of pharmaceutical-grade products like FDA-approved HGH.
When administering HGH or any other hormone, ongoing evaluation by an experienced endocrinologist is an indispensable aspect of the therapy that safeguards the health of the patient.
Whereas HGH replacement therapy can be performed under such clinical supervision, monitoring the health of individuals who take steroids is impossible due to the illegal status of the drug.
Growth Hormone vs. Steroids: What You Should Take Away
As elaborated in this article, HGH and steroids are not the same thing, although the reasons that someone may confuse them are understandable.
Anabolic steroid use is strictly prohibited by law under all conditions. There are no recognized medical purposes for anabolic steroid abuse, and individuals who utilize these supplements in contravention of the law or doctors who prescribe them unethically to their patients face harsh legal consequences. Furthermore, illegal steroid abuse causes a number of serious and often irreversible detrimental health impacts, many of which we discussed earlier.
HGH replacement therapy, on the other hand, is a recognized medical practice that offers an array of benefits to patients with diagnosed HGH deficiencies who receive the treatment, including boosted athletic performance.

