Male sperm counts have been falling in North America, Europe, Australia, and New Zealand for decades. The fallout is so intense, in fact, that some researchers estimate that sperm counts have dropped by more than half in just the past 40 years. These unsettling developments in men’s sexual health have signaled what many experts call a “fertility crisis” throughout the West.
If you’re an American man over 30, chances are that the infertility epidemic has affected your reproductive health. Later on, we’ll discuss strategies for restoring it.
First, though, we’ll explore what is driving the fertility crisis that has compromised the virility of so many men.
How Is “Male Fertility” and How Is It Measured?
The term “male fertility” refers to a man’s ability to successfully impregnate a female partner through intercourse. A man’s fertility is often closely interwoven with his identity as a male, so health issues affecting his sexually virility hit home. Understandably, many men who battle fertility issues are hesitant to share their challenges due to social stigma.
However, as we’ll discuss, male fertility is more common than you likely think, and the strategies for restoring it are relatively straightforward. There’s no reason to accept infertility as a “fact of life” or to be embarrassed about it.
How Do Physicians Screen for Infertility?
Fertility in men is measured by collecting a semen sample and then analyzing it. If a doctor notices any concerning symptoms or assesses a possibility of infertility based on the risk factors explained below, he or she will order lab work to check the quantity and potency of the patient’s sperm.
Assessing Sperm Count
Analyzing overall sperm count is one of a battery of clinical tests necessary to accurately diagnose fertility issues. To do the test, patients are typically required to ejaculate into a cup to be delivered to a lab to be studied. In addition to checking the total number of sperm in the count, the lab staff will also check for sperm motility and morphology.
Assessing Sperm Motility
“Sperm motility” refers to sperm’s capacity to move once it is introduced through ejaculation into the female’s reproductive tract. Once sperm is released following climax, they must “swim” to reach the egg and penetrate it to fertilize it. As high as 50% of all infertility cases are actually caused by sub-optimal sperm motility and not due to the quality of the sperm itself.
Assessing Sperm Morphology
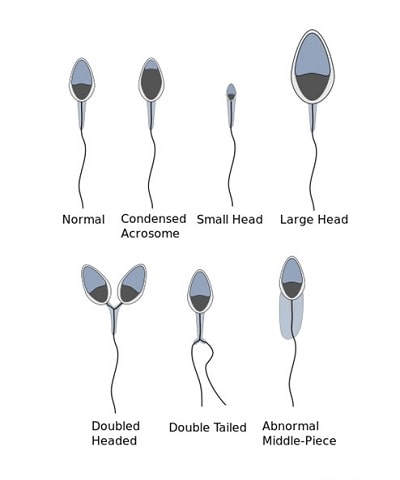
“Sperm morphology” involves the microscopic analysis of a sperm’s shape. Lab technicians examine samples under a microscope to ascertain their shape. A high concentration of irregularly-shaped sperm indicates a potential barrier to contraception, although many men with unusual sperm morphology can successfully impregnate their partner.
The image below illustrates the various shapes that sperm often take which diverge from normalcy.
What Factors Affect Male Fertility?
The following factors can negatively impact male fertility:
- Depression and anxiety.
- Exposure to toxins.
- Sexually transmitted infections (STIs).
- Obesity.
- Alcohol use.
- Illicit drug use.
- Nicotine use.
- Pharmaceutical medications.*
*In this article, we’ll focus on how popular, frequently prescribed medications like antibiotics harm male sexual health.
Each of these factors alone can harm male fertility. When a man exhibits two or more of these risk factors “stacked” together, as is often the case, their risk for infertility increases.
What Are the Dangers of Common Medications For Male Fertility?
Pharmaceutical drugs often come with a lengthy list of potential side effects, usually written in fine print on the backside of an insert. Unfortunately, many Americans simply ignore the warnings highlighting the potentially devastating impacts of these drugs on their health, including the implications for fertility. Even worse, many doctors fail to provide adequate warning to their patients about the potential risks associated with medications they prescribe.
In this article, we’ll focus on the most serious pharmaceutical threats to male fertility from over-prescribed antibiotics like penicillin, antidepressants like SSRIs, and similar drugs.
What Effect Do Medications Like Antibiotics Have on Testosterone Levels in Men?
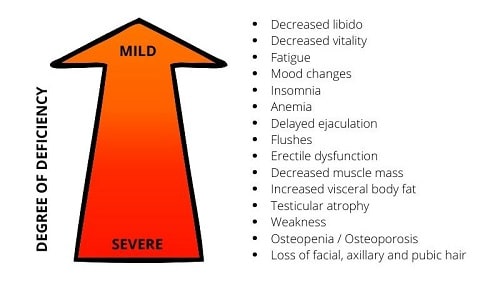 As the primary male sex hormone, testosterone in healthy levels is crucial for male fertility. Sadly, common drugs can substantially diminish free testosterone levels (the kind needed for optimal sperm production) in circulation, leading to infertility in many instances. Testosterone deficiencies carry a number of serious health consequences for men in addition to affecting sperm counts.
As the primary male sex hormone, testosterone in healthy levels is crucial for male fertility. Sadly, common drugs can substantially diminish free testosterone levels (the kind needed for optimal sperm production) in circulation, leading to infertility in many instances. Testosterone deficiencies carry a number of serious health consequences for men in addition to affecting sperm counts.
The following drugs are known through clinical research to deplete testosterone supplies in men:
- Opioid pain relievers. In addition to fueling the ongoing public health crisis surrounding opiate addiction, these dangerous drugs also lower testosterone counts in men. Opioid drugs threaten healthy testosterone levels by disrupting the activity of the hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal axis (HPG axis). Researchers have observed that opioid addiction renders testosterone levels down to “near-castrate” levels, meaning that opioid drugs reduce testosterone quantity to those to a man whose testicles have been removed. In the US, typical examples of often-prescribed opioids are hydrocodone (Vicodin) and oxycodone (OxyContin).
- Ketoconazole. Often marketed as Ketoderm, Extina, or Nizoral, this medication is often prescribed to patients to treat yeast or fungi infections. It comes in both pill and cream form.
- Statins. Statins are the single most widely-prescribed class of drugs for the treatment of high cholesterol. Although they benefit heart health in at-risk patients, these drugs also cause “small, but statistically significant” testosterone reductions in men who take them. Well-known brand names for statins include Lipitor and Lescol.
- Spironolactone. Spironolactone is prescribed to heart patients. It works primarily by preventing fluid accumulation in people with heart failure and similar conditions. It is also shown to be effective in reducing blood pressure. Spironolactone is most commonly available in the US under the brand name Aldacton.
- Chemotherapy drugs. Chemotherapeutic agents like Alkylating drugs and others are linked to declines in men’s testosterone levels, in addition to a link between cancer itself and low testosterone. These drugs are known to inhibit the activity of Leydig cells, where testosterone is produced. In cancer patients administered testosterone replacement therapy (TRT), their prognosis for recovery from radiation treatment improved.
The drugs listed here represent only a smattering of the many pharmaceutical medications that likely interact negatively with the endocrine system to lower testosterone. As a rule of thumb, carefully read the contraindications and reported side effects of drugs before you consume them to avoid unexpected declines in testosterone due to your medication.
What Drugs Can Affect Male Spermatogenesis?
 “Spermatogenesis” is the medical term for the development of sperm within the testicles. In healthy men, viable sperm are produced in normal quantities where they are temporarily stored until they are ejaculated through the penis.
“Spermatogenesis” is the medical term for the development of sperm within the testicles. In healthy men, viable sperm are produced in normal quantities where they are temporarily stored until they are ejaculated through the penis.
As well as harming testosterone levels, some drugs are also known to negatively alter the spermatogenesis process, thereby limiting a man’s ability to fertilize a female partner’s eggs. Three of the most common medications that affect sperm production are mycophenolate mofetil, azathioprine, and sulfasalazine.
What Antibiotics Affect Sperm Counts?
“Antibiotics” serves as the umbrella term for any drug that has therapeutic value for humans by killing harmful bacterial pathogens that cause disease. Antibiotics have an incredibly important historical value in medicine, having helped achieve the elimination or control of previously life-threatening illnesses like Staphylococci (staph) infections that often turn deadly if left untreated.
However, most doctors and researchers now agree that antibiotics are massively overused in the modern era. While the overuse of antibiotics has triggered serious public health concerns like antibiotic-resistant bacteria that have adapted to overcome these drugs, antibiotics can also cause uncomfortable and unhealthy side effects in patients who take them.
Aside from relatively minor side effects like diarrhea and nausea, the consequences of overusing antibiotics can also sometimes include:
- Blood clotting disorders.
- Sunlight sensitivity.
- Kidney stones.
- Lowered sperm counts.
Although there is evidence that antibiotics do not lower testosterone levels, there is plenty of evidence that they can harm sperm counts, even in otherwise healthy men who take them.
Studies that examined the ejaculate quality of men treated with antibiotics compared to untreated men found that common medications used to kill harmful bacteria have demonstrable, negative impacts on both the quantity and quality of sperm.
 The following drugs are proven to lower sperm counts:
The following drugs are proven to lower sperm counts:
- Nitrofurans. Doctors actually use Nitrofurans to intentionally imbolize sperm in certain clinical situations. For men who want to keep their swimmers active, though, they should avoid this antibiotic whenever possible.
- Aminoglycosides. Aminoglycosides are often used to treat staph and similar bacterial infections. Unfortunately, their use also results in decreased sperm viability and motility in men.
- Macrolides. Macrolides rank among the most frequently used antibiotics in the world. They induce death in pathogenic bacteria by inhibiting protein synthesis, thereby preventing reproduction. Macrolides are frequently employed clinically to battle Streptococcus pneumoniae bacteria (the cause of strep throat) and other infections caused by gram-positive bacteria. Common brand names of macrolides include Biaxin, Zithromax, and Erythromycin. Macrolides hamper spermatogenesis by preventing appropriate cell division necessary for sperm production.
- Sulfonamide. Commonly referred to as “sulfa drugs,” this class of antibiotics stunts bacteria growth and biosynthesis, effectively killing them, by cutting off their access to folate necessary for reproduction.Sulfa drugs harm male fertility by reducing sperm concentrations and sperm mobility.
- Penicillin. In terms of popular use, penicillin is king among the antibiotics. It is the most widely used antibiotic in the modern medical arsenal.
Although more research is needed on the potential effect that penicillin might have on fertility, it appears to be the least harmful among common antibiotics in terms of compromising men’s sexual health.
How to Avoid Antibiotics That Lower Sperm Counts and Quality
The reality in the developed world, including the US, is that we rely too heavily on antibiotics too often, even in situations where the help they might offer is negligible. To protect your sexual vitality, carefully weigh the potential benefits and risks associated with antibiotic use before beginning a treatment protocol. Ask your doctor about the possibility of lowered sperm counts and/or diminished sperm quality.
 Every day across the US, in routine clinical situations, doctors prescribe excessive amounts of antibiotics — for example in the treatment of common STI infections. While these drugs can be effective treatments, their repetitive use also carries substantial downsides to our well-being, including for sexual health.
Every day across the US, in routine clinical situations, doctors prescribe excessive amounts of antibiotics — for example in the treatment of common STI infections. While these drugs can be effective treatments, their repetitive use also carries substantial downsides to our well-being, including for sexual health.
Aside from avoiding extraneous antibiotic medications, you should also weigh the risks posed by the excessive application of antibiotic therapies in commercial agriculture.
Public health experts have warned for years that antibiotic-laden animal products threaten human health when they are used at the rates that we see today in the commercial dairy sector, for example.
You can avoid antibiotics in your food by selecting foods that have been certified antibiotic-free.
Can Antidepressants or Other Drugs Affect Male Sexual Health?
Many clinicians, to the detriment of their patients’ health, regularly overlook the close link between testosterone levels in men and depression. As a result, we can safely guess that lower testosterone levels across the board have contributed significantly to what experts call the “mental health crisis” that has witnessed millions of American men prescribed to prescription drugs intended to treat depression and anxiety.
Two of the most common medications for the treatment of mental health conditions are serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) and benzodiazepines like alprazolam (Xanax) and diazepam (Valium).
The Impact of Depression Medications on Male Sexual Health
Because of skyrocketing rates of depression in the US and across the Western world, antidepressant medications like SSRIs have become some of the most commonly prescribed drugs in the US. The American Psychiatric Association estimates that, in 2017, 12-13% of the total population over the age of 12 regularly used SSRIs to treat mental health issues.
If you browse the web, listen to the radio, or watch TV, chances are you’ve seen plenty of advertising for SSRIs. These drugs generate enormous profits for pharmaceutical companies, leading to massive marketing campaigns for more customers, in turn driving their overuse among Americans. The following SSRI drugs top the list of the most frequently prescribed drugs for the treatment of depression:
- Escitalopram. (Lexapro)
- Citalopram. (Celexa)
- Sertraline. (Zoloft)
- Paroxetine. (Paxil)
- Fluoxetine. (Prozac)
Research into the effects of SSRIs on male sexual health shows that these drugs exert a “negative effect” on tissues in the testicles, although the study’s authors indicate the need for more research on the topic to understand the mechanism by which SSRIs impact testicular tissues.
How Benzodiazepines for the Treatment of Anxiety Affect Male Sexual Health
 In addition to SSRIs, Americans take benzodiazepines in record numbers. Each year, US physicians write tens of millions of prescriptions for Xanax, Klonopin, Ativan, Valium, and their generic versions for their remarkable short-term ability to stop panic attacks and their anxiolytic (anxiety-killing) properties. The anxiolytic activity of benzodiazepines is owed to their work on the GABA neurotransmitter system, one of the signaling systems for nervous system relaxation. Alcohol works on the same GABA system.
In addition to SSRIs, Americans take benzodiazepines in record numbers. Each year, US physicians write tens of millions of prescriptions for Xanax, Klonopin, Ativan, Valium, and their generic versions for their remarkable short-term ability to stop panic attacks and their anxiolytic (anxiety-killing) properties. The anxiolytic activity of benzodiazepines is owed to their work on the GABA neurotransmitter system, one of the signaling systems for nervous system relaxation. Alcohol works on the same GABA system.
Benzodiazepines wreak havoc on male fertility. One study on diazepam (Valum), for example, scientists noted a “significant fall” in blood concentrations of testosterone. If you are regularly prescribed either SSRIs or benzodiazepines and are concerned about their potential impacts on fertility, discuss alternative treatment options with your doctor. Do not attempt to quit either of these types of drugs cold-turkey due to potentially devastating withdrawal symptoms, including life-threatening seizures.
The Bottom Line on Antibiotics and Other Drugs on Male Fertility
The facts as we’ve laid them out in this article, using the available scientific data to inform our conclusions, indicate that modern American medicine’s overdependence on antibiotics and other drugs has significantly harmed men’s fertility in the US and abroad. Antibiotics, as well as the other drugs, discussed earlier, impair a man’s ability to successfully produce viable new sperm, diminishes overall sperm quality, and lowers testosterone levels that are crucial for optimal sperm production.
If one or more of the common medications highlighted here have negatively affected your sexual health, testosterone replacement therapy (TRT) designed to restore healthy concentrations of testosterone in the blood could be a viable treatment option to recapture your vitality.

