There’s no way to sugarcoat the reality that runaway obesity among American men is a major public health crisis that requires attention. Technology has afforded us many benefits in terms of quality of life, but the conveniences of modern living have come at a cost to our health. We eat too many processed foods, exercise too infrequently, and miss out on testosterone-boosting sleep – all of which contribute to weight gain.
What the Data Says About Male Obesity and Testosterone
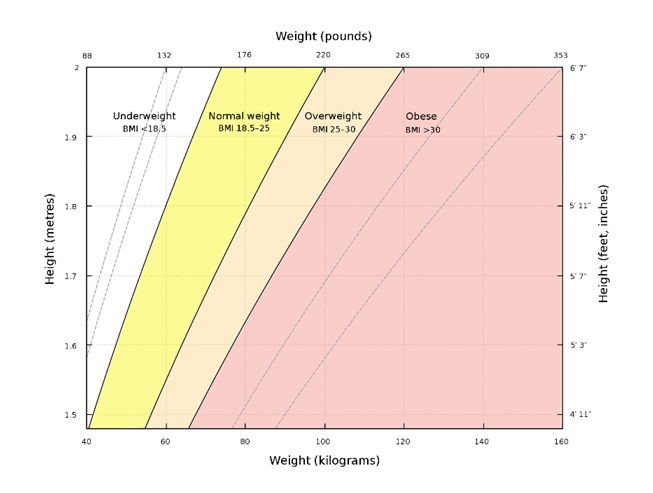 Medical professionals worldwide utilize Body Mass Index (BMI) scale as the standard measurement of obesity. The technique involves a mathematical formula of weight divided by height to calculate ideal body weight. The BMI scale breaks down like this:
Medical professionals worldwide utilize Body Mass Index (BMI) scale as the standard measurement of obesity. The technique involves a mathematical formula of weight divided by height to calculate ideal body weight. The BMI scale breaks down like this:
- BMI = <18.5 — Underweight
- BMI = 18.5 to <25 — Normal
- BMI = 25.0 to <30 — Overweight • BMI = >30.0 – Obesit
To better illustrate how BMI is calculated, have a look at this chart:
Using the BMI standard, a stunning 55% of adult Americans are now overweight or obese. Even worse for our public health, obesity rates have steadily climbed for decades as we drive more, walk less, eat processed food on the go, and sleep fewer hours.
*A note on BMI measurements: Many health experts criticize the BMI scale as too simplistic because, among other issues, it does not take into account body fat vs. lean muscle ratios. So, for example, an athlete in prime physical condition who happens to have well-developed muscles might quality as overweight when the BMI formula is applied even though, in reality, he is healthy. Therefore, BMI measurements should be taken with a grain of salt.

Men with hormone deficiencies who come to our clinic for help often express concern about the potential impact that their low testosterone levels might be having on their weight loss efforts or, conversely, the effect that their weight might have on testosterone production.
One study found that men with excess body fat have an average of 30% less circulating testosterone than men who maintain a healthy weight.
Understanding the Cycle of Testosterone Loss and Weight Gain
A key to understanding the relationship between weight gain and testosterone deficits in the body is that one affects the other and vice versa. Low testosterone contributes to fat retention, especially in the belly as we’ll discuss later, while higher fat deposits in the bodywork to lower testosterone.
This kind of activity of testosterone on body fat and body fat on testosterone levels can create a negative health spiral of chronically lowered testosterone paired with ever-increasing body fat. Stemming this negative spiral depends on taking decisive and impactful steps to reverse the trend.
How does low T cause weight gain and what can you do about it? We’ll explore the complex relationship between body fat and testosterone here.
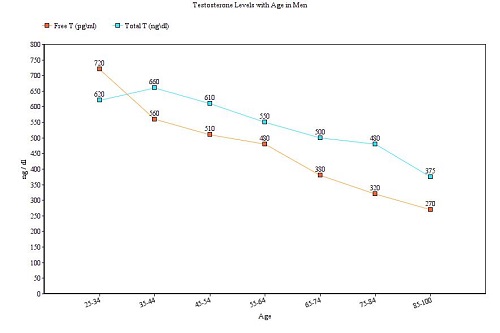
Production of Testosterone in the Body
Testosterone is the most important male sex hormone. Its primary purposes are to stimulate secondary sexual characteristics in men like body hair and muscle growth, to induce sexual arousal, and to facilitate sperm production.
Both men and women produce testosterone naturally. However, men produce the hormone in much higher quantities because their physiological processes require more. In men, the testes primarily are responsible for testosterone production, although adrenal glands also make a small contribution of testosterone.
The production of testosterone ramps up significantly in men during puberty. It skyrockets to an all-time high around the age of 20, then slowly declines year by year. As men age, they typically lose one percent per year of this vital male sex hormone. As a result, they often see the symptoms of low testosterone described earlier – including unwanted increases in body fat. This chart demonstrates the gradual decline of testosterone levels as we age. Here, “free testosterone” refers to the type of the hormone that your body “freely” uses because it is not bound to any other molecules. When medical professionals discuss testosterone levels, they are usually referring to free testosterone.
The slowdown/reversal of declining testosterone levels is achievable through both lifestyle modification and supplementation through testosterone replacement therapy (TRT). We will discuss the potentially enormous benefits of TRT for men with deficiencies further as we move along.
Does Testosterone Burn Fat?
The evidence is clear that testosterone incinerates adipose tissue, commonly known as body fat. In recent years, we’ve learned through research more of the complex interactions between testosterone and body fat.

The Curse of Belly Fat: Low Testosterone and Abdominal Fat
Getting rid of belly fat should be the primary goal of anyone who wants to lose weight. The fat that accumulates around the belly is particularly harmful to overall health it can cause a host of chronic conditions, including diabetes, heart disease, and cancer.
Belly fat also negatively impacts testosterone because it contains aromatase in higher concentrations than other fat stores. Aromatase is detrimental to healthy testosterone levels because it converts the hormone into estrogen through a process called aromatization. Losing belly fat results in higher testosterone.
Testosterone Protects Muscle While Shedding Fat
Many men who embark on weight loss journeys are worried about losing muscle in addition to fat. Fortunately, when men modulate their diets to lose weight, testosterone protects a man’s lean muscle mass while shedding fat at the same time. Researchers gave one group of clinically obese men testosterone and gave a placebo to the other group. Then, the subjects were placed on a hypocaloric diet (meaning a meal plan that includes fewer calories than the body burns for energy), inducing weight loss as the body made up for calories it did not receive through food.
The results of the study showed that, after 46 weeks, the group that had been administered testosterone had shed body fat without losing muscle mass. The control group, which had not been given supplemental testosterone, lost both body fat and muscle. In times of caloric deficits, such as during weight-loss diets, testosterone signals metabolically to the body that it needs to keep its muscle. For any man who wants to lose body fat but not muscle, ensuring proper testosterone levels is a must to stay strong and lean.
Maintaining higher muscle mass contributes to sustained weight loss because muscle requires a high caloric commitment which burns more calories and prevents fat accumulation.
Hypogonadism and Weight Gain
Hypogonadism is the medical term for conditions in which the testes do not produce an adequate supply of testosterone to meet the body’s needs. It is a serious condition that requires corrective action.
Left untreated, hypogonadism impairs quality of life and contributes to disease. Among the many negative consequences of hypogonadism, unwanted weight gain is one of the most common.
The two types of hypogonadism are:
- Primary hypogonadism. In cases of primary hypogonadism, the issue is traced through testing to the testicles. For a variety of reasons, the testes might fail to produce testosterone in desired quantities. Diseases like Noonan syndrome and Turner syndrome are examples of this type of testosterone deficiency.
- Secondary hypogonadism. In cases of secondary hypogonadism, the reason for limited testosterone production is caused by a defect outside of the testes. In patients with this type of testosterone deficit, inadequate levels of follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH) inhibit testosterone production.
Research shows that obesity causes hypogonadism and, conversely, hypogonadism contributes obesity. The two conditions are closely linked, but scientists remain unsure of exactly why the two conditions contribute to each other’s development.
Testosterone Replacement Therapy for Hypogonadism
TRT to treat hypogonadism, in this study, caused accelerated weight loss while simultaneously stimulating muscle development –making it an excellent choice for many men experience testosterone deficiencies. We’ll discuss who might be a good candidate for TRT a little later.
Causes of Low T in older men
 WordThe human hormone system is complex. Many factors can affect testosterone levels. Aside from specific conditions like Noonan syndrome discussed earlier, rarely is one identifiable cause the only factor in low T. The following can all affect testosterone levels in the body:
WordThe human hormone system is complex. Many factors can affect testosterone levels. Aside from specific conditions like Noonan syndrome discussed earlier, rarely is one identifiable cause the only factor in low T. The following can all affect testosterone levels in the body:
- Activity levels. Exercise, especially weightlifting, is closely linked to optimal hormone levels. Men who work out regularly have higher levels of testosterone while mostly inactive men are at a higher risk of low T.
- Age. As we mentioned earlier, testosterone levels peak around age 20 and then slowly drop each year. Men over 40 are at a higher risk of low T than younger men.
- Medications. Several medications like common SSRIs for depression and drugs to treat the damaging effects of cancer radiation can severely impact testosterone production.
- Diet. Unfortunately, the modern American diet is seemingly designed to kill testosterone. For healthy testosterone levels, men should eat more whole foods-based diets rich in healthy, lean protein sources like fish as well as plenty of green vegetables, especially members of the cruciferous family such as broccoli and kale, and less processed food.
- Injury. Occasionally, trauma to the testicles can inhibit blood flow to and from the testicles, in turn lowering testosterone. Testicular infections, called orchitis, can also negatively impact testosterone levels.
Diagnosing Low T
Low testosterone levels, often called low T for short, is a common health problem among men over 40, although it can affect a man at any age. Symptoms of low include:
- Chronic fatigue.
- Loss of sexual desire.
- Inability to get or maintain an erection.
- Loss of muscle mass.
- Increased body fat.
How to Safely Increase Testosterone to Enhance Weight Loss
The following methods are proven to be effective at elevating testosterone levels and, in turn, aiding in weight loss for men who have low T:
- Sleep. The average man requires a minimum of 7 hours of sleep to produce the necessary amount of testosterone for optimal health.
- Vitamin D exposure. The sun provides an ample supply of this much-needed sunshine vitamin. One study found that testosteorne levels rebounded significantly in men with low T after supplementation. Vitamin D also plays an important role in maintaining a healthy weight.
- Anabolic exercise. The benefit of weightlifting as a component of treatment for low T cannot be overstated. Although weightlifting is the most effective for lifting testosterone levels, all forms of exercise boost testosterone to some degree.
- Relaxation Techniques. Stress is a major known testosterone killer. Incorporating mindfulness meditation, breathing techniques, or other relaxation practices into your daily routine can help prevent the loss of testosterone due to stress.
- Testosterone Replacement Therapy. TRT, in combination with the other testosterone-boosting methods listed here, is extremely effective at boosting T levels in most cases.
Could TRT Help Me Lose Weight?
Because of the close link between testosterone levels and body fat, the renowned health organization The Endocrine Society recommends TRT as a safe and effective weight-loss method for many men who have testosterone deficiencies.
Getting Started on Testosterone Replacement Therapy
To begin your testosterone enhancement and weight loss journey, give our friendly staff a call today. We’ll schedule an appointment for you to visit our friendly, welcoming clinic to discuss your specific health concerns and what benefits TRT can offer you.
Our team of dedicated doctors specializing in hormone replacement takes the time to consult with each patient to answer any questions, run necessary diagnostic tests, and develop an individualized treatment plan to help you reach your health goals.

